The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul, stands as a unique and efficient writing system. Created during the 15th century under the reign of King Sejong during the Joseon Dynasty, Hangul is comprised of 14 basic consonants and 10 basic vowels. These characters are arranged into syllabic blocks, and the writing system is notably phonetic, allowing for a straightforward pronunciation guide.
Here is the Korean alphabet (Hangul) with their corresponding romanization:
ㄱ - g
ㄴ - n
ㄷ - d
ㄹ - r/l
ㅁ - m
ㅂ - b
ㅅ - s
ㅇ - (silent at the beginning of a word; pronounced as ng at the end of a syllable)
ㅈ - j
ㅊ - ch
ㅋ - k
ㅌ - t
ㅍ - p
ㅎ - h
ㅏ - a
ㅑ - ya
ㅓ - eo
ㅕ - yeo
ㅗ - o
ㅛ - yo
ㅜ - u
ㅠ - yu
ㅡ - eu
ㅣ - i
Additionally, there are combinations of consonants and vowels to form syllables in Hangul.
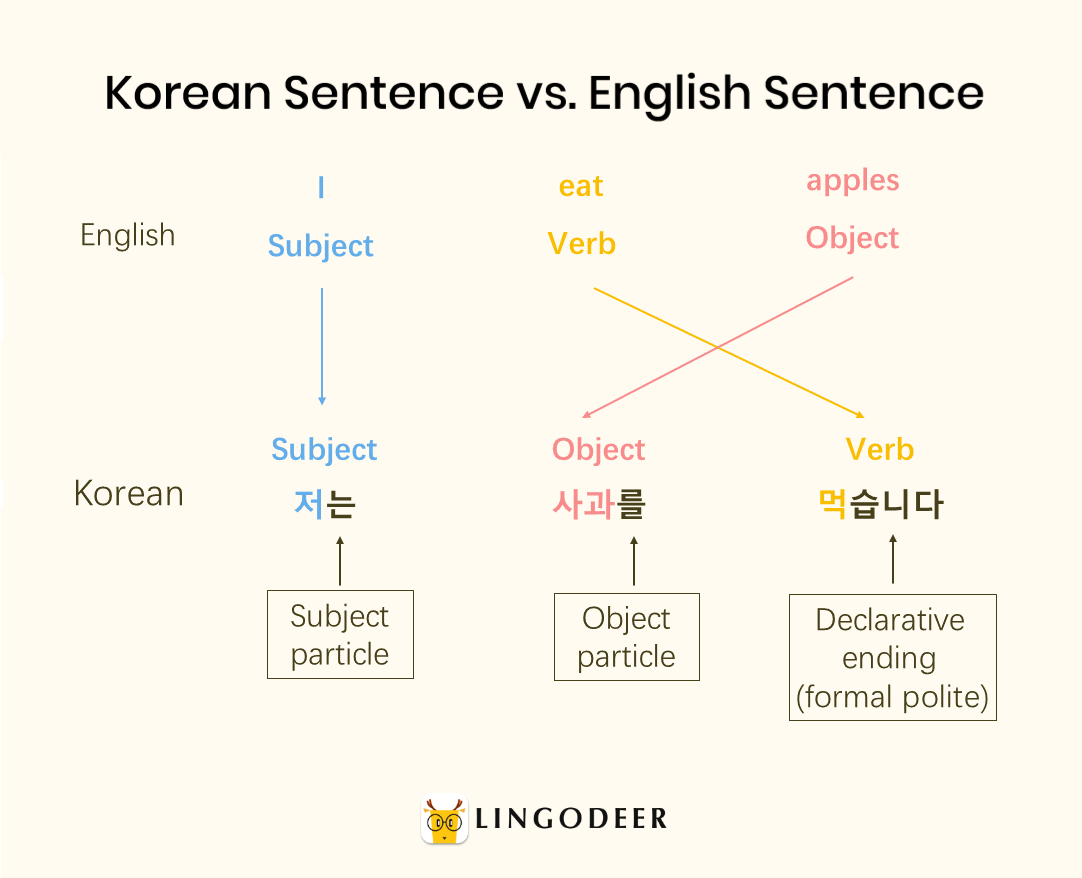
Hangul, the Korean writing system, is paired with a relatively simple and logical grammar structure that facilitates ease of learning. Unlike some other languages, Korean sentences often follow a subject-object-verb (SOV) order, placing emphasis on the action. Subjects are usually marked by particles such as "이" (i) or "가" (ga), while objects receive markers like "을" (eul) or "를" (reul). Verbs remain largely unchanged regardless of tense or person, with context and particles providing clarity. Furthermore, Korean employs honorifics and politeness levels to reflect the speaker's relationship with the listener. The absence of grammatical gender and the use of context-driven particles contribute to Hangul's reputation for user-friendly grammar, making it accessible for learners.